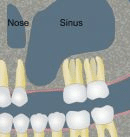
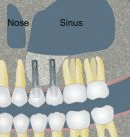
In fact, dental implants do have one constraint... In order to place an implant reliably, sufficient bone volume is required. In the upper jaw, above the molars, there is a hollow cavity in the middle of the jawbone, this "pneumatic cavity": it is the maxillary sinus. The maxillary sinus is lined with a mucous layer: this is Schneider's membrane. Very often, when the maxillary molars are extracted, the amount of residual bone under the maxillary sinus is too small to be able to place implants (at least 6-8 mm of bone is needed to place an implant).
What to do?
As early as the 1970s, practitioners had the idea of performing a bone augmentation under the maxillary sinus, by removing Schneider's membrane and interposing a filling material.
Today, there are two techniques for bone augmentation under the sinus:
- Elevation and partial filling of the maxillary sinus by the alveolar (or crestal) route, known as the Summers technique.
- Elevation and partial filling of the maxillary sinus using the Tatum technique or " Sinus Lift ".
These two techniques have different indications.
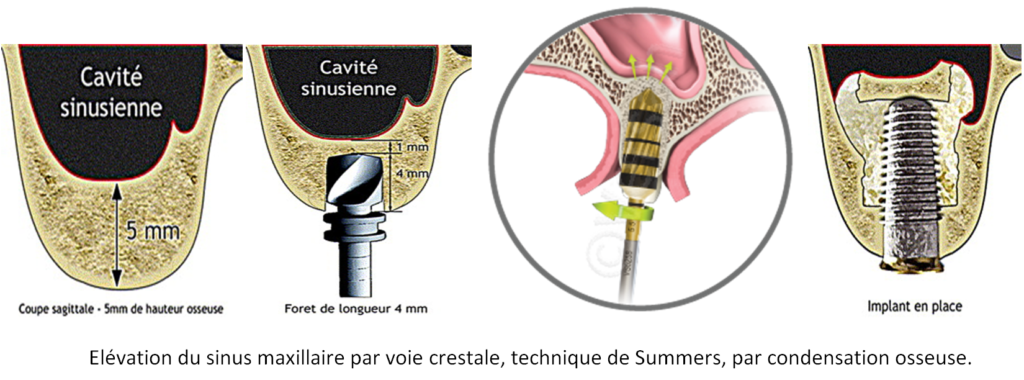
Summers' technique
The Summers technique can be used when at least 4-5 mm of bone remain under the sinus. It involves "pushing" the sinus membrane through the alveolus created for implant placement. Today, this elevation is achieved using special drills that rotate in opposite directions, collecting bone shavings during drilling, condensing them and gently injecting them under the sinus membrane, which is then gently pushed. Depending on the bone volume to be gained, a filling material can be interposed before the implant is placed, in the same operating time. The post-operative course is generally minor.
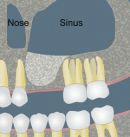
Sinus Lift
Le Sinus Lift est réservé aux pertes osseuses plus importantes (hauteur résiduelle < 4-5 mm). Il s’agit de réaliser une fenêtre osseuse en regard du sinus maxillaire, puis la membrane de Schneider est minutieusement décollée. Un matériau de comblement est ensuite glissé sous cette membrane, et la fenêtre est refermée. Il est parfois possible de placer les implants en même temps, mais dans la plupart des cas, il est préférable de laisser cicatriser 3-4 mois et de poser les implants après un contrôle radiographique 3D. Les suites postopératoires sont plus importantes qu’avec la technique de Summers, elles sont comparables à l’extraction de dents de sagesse incluses. Œdème et hématome surviennent parfois.
Benefits
These two meticulous operations require a large technical platform and an experienced team. This is why Dr Michaël LUMBROSO holds a University Diploma in Maxillofacial Rehabilitation Surgery(University of Paris VII), and is fully qualified to carry out this type of operation. Indeed, the main risk of these operations is a tear of Schneider's membrane without the practitioner noticing it.
This is why in our practice these operations are performed in our Operating Theatreunder rigorous aseptic conditions (Sterilization chain HEPA filter, Traceabilityetc ...). During a Sinus Lift, in order to limit as much as possible the risk of tearing the Schneider's membrane, we use a very special equipment: the PIEZZOCHIRURGY. This instrument uses ultrasound and allows the bone window to be made without damaging the membrane underneath, as it is inactive on the soft tissue.
Furthermore, in our practice, this procedure is performed under an operating microscope. This considerably increases the precision of our actions, and thus reduces the risk of tearing the membrane. And if a perforation should occur, it is almost impossible for it to go unnoticed thanks to the operating microscope. The operation is then stopped and the window closed, without any consequences for the patient's health. However, it will be necessary to intervene again after a few weeks.
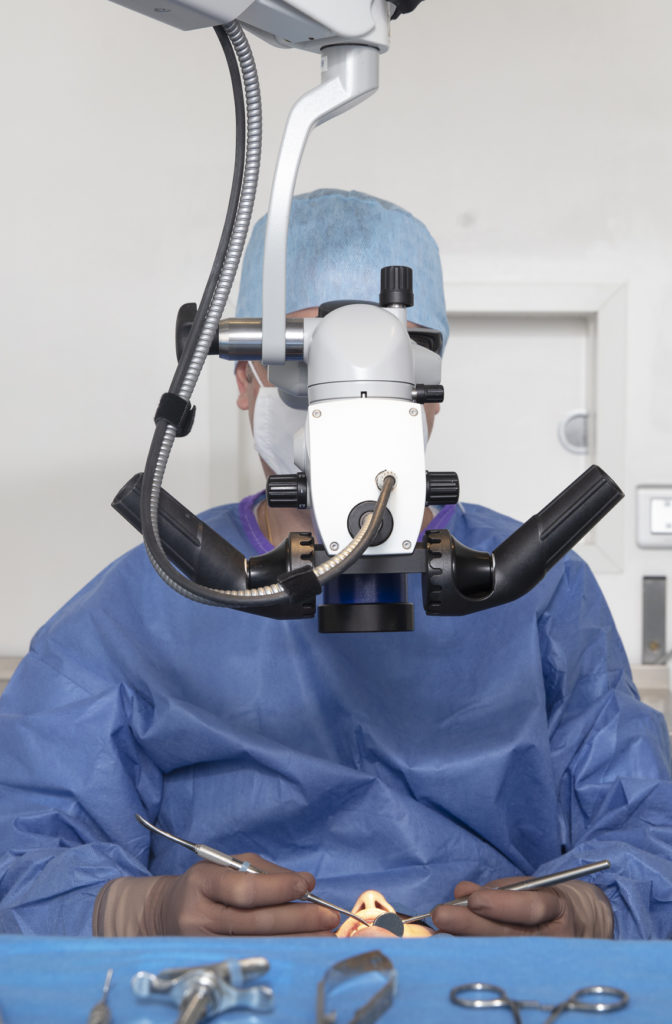
For this type of bone augmentation procedure, strict hygiene and aseptic conditions are required, and an operating theatre is preferable.
The French National Authority for Health (HAS) published a summary in 2008 on these subjects ("conditions for performing oral implantology procedures: technical environment"): "Bone ridge expansion, techniques using osteotomes such as Summers osteotomies, sinus floor enhancement with the use of intraoral bone harvesting material or bone substitute material and bone autografts can be performed in specific or adapted operating rooms or in the operating theatre. "
